The interplay between hormonal changes, stress, and sleep deprivation often makes breastfeeding moms more susceptible to migraine.
Additionally, sorting through safe pain relief options while nursing can feel overwhelming.
For many mothers, the desire to provide the best nutrition for their child while managing their own health can create stress and anxiety.
On the other hand, breastfeeding can suppress the menstrual cycle and lead to stable hormone levels while breastfeeding, which can also have a migraine protective effect.

It's important to understand how breastfeeding can affect migraine and what options are available to manage this condition without compromising your nursing journey.
This article will provide an overview of what to expect when breastfeeding as a migraine patient, what happens to hormone levels and what might be safe migraine management strategies during the time of nursing.
By understanding your migraine better and adopting practical management techniques, you can navigate breastfeeding while minimizing discomfort and maintaining a strong bond with your baby.
Let’s dive in to empower yourself with valuable knowledge and actionable tips for managing migraine effectively during this crucial time.
Hormonal Changes During Nursing Journey
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, hormonal fluctuations can significantly influence migraines, particularly in individuals prone to hormonal migraine.
To understand what happens during breastfeeding, it is important to also understand what happens before.
The key hormones—estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, and oxytocin—play distinct roles:
Pregnancy, hormones and migraine:
- Estrogen: During pregnancy, estrogen levels rise steadily, leading to greater hormonal stability. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with menstrual migraines, as fluctuations in estrogen are a common trigger. Estrogen is a strong antioxidant and further protective. Many experience a reduction or complete remission of migraines in the second and third trimesters when estrogen levels stabilize.
- Progesterone: Elevated progesterone contributes to the relaxation of blood vessels, which may reduce migraine frequency. However, in early pregnancy, when progesterone and estrogen levels are still adjusting, some individuals may notice temporary worsening of migraines.
- Cortisol: Increased cortisol during pregnancy can influence migraines. Cortisol is important to ensure energy availability for the fetus and mother and migraine is known to come with energy deficiency. During very bad and long migraine episodes, in an emergency setting cortisol infusions are known to help, so this is another factor that can positively impact migraine.
- Oxytocin: Although oxytocin levels are low during most of pregnancy, its rise near labor helps trigger uterine contractions. Oxytocin’s pain-relieving properties may also play a role in reducing the intensity of migraines during labor and postpartum bonding.
Postpartum and Breastfeeding and its hormonal influences on migraine:
- Estrogen and Progesterone: After delivery, estrogen and progesterone levels drop sharply, which can trigger postpartum migraines. This hormonal withdrawal is a significant factor for those with a history of menstrual migraines. One loses the protective effect of high Estrogen. On the other hand, as estrogen levels remain low but stable during breastfeeding, some individuals experience reduced migraine frequency while breastfeeding, due to the lack of fluctuation.
- Cortisol: Postpartum stress and sleep deprivation can disrupt cortisol levels, potentially triggering migraines. Managing stress and ensuring adequate rest are crucial during this period.
- Oxytocin: During breastfeeding, oxytocin helps with milk ejection and promotes relaxation and bonding. Its natural pain-relieving properties can help reduce migraine severity during breastfeeding sessions.
Key Takeaways
- The stabilization of estrogen during pregnancy often leads to a reduction in migraines, especially in the second and third trimesters.
- Postpartum hormonal shifts, sleep deprivation, and stress can exacerbate migraines.
- Breastfeeding may help regulate migraines through sustained low estrogen levels and the pain-modulating effects of oxytocin.
Understanding these hormonal influences can help in managing migraines during pregnancy and breastfeeding. You're not alone; many new mothers face similar challenges.
These hormonal shifts can be challenging, but understanding them is the first step in managing your migraine effectively.
You might find relief through non-pharmacological treatments like maintaining a headache diary to identify triggers, ensuring proper hydration, and sticking to regular meal schedules.
Techniques such as biofeedback, massage, and acupuncture can also be beneficial.
It's important to discuss with your healthcare provider which complementary therapies are safe during breastfeeding.
When it comes to safe medication options, there are choices that won't jeopardize your baby's health.
Always consult with your doctor to tailor a treatment plan that balances migraine relief with breastfeeding safety. Your well-being and your baby's health are both priorities.
Physical Demands on Nursing Mothers
As a breastfeeding woman, the stability in hormone levels often offers a protective shield against migraine compared to non-breastfeeding mothers.
However, managing migraine during this phase requires balancing your needs and your baby's safety.
Ensuring proper hydration is essential, as breastfeeding can deplete fluids quickly, potentially triggering migraine.
Adequate sleep is another cornerstone for managing migraine, but it can be elusive with a newborn.
Prioritizing rest whenever possible can help mitigate migraine attacks.
Nutrient deficiencies might arise due to the nutrient-rich nature of breast milk, so maintaining a balanced diet and possibly supplementing is crucial.
When it comes to migraine treatments, consulting with your healthcare provider about safe migraine medications is vital.
Many medications might be transmitted through breast milk, so selecting options that prioritize your baby's well-being is essential.
Non-pharmacological approaches, such as biofeedback and relaxation techniques, can be effective supplements to your migraine management strategy.
Natural Relief While Nursing
Incorporating proven non-drug therapies like massage, acupuncture, and relaxation techniques can offer relief without compromising your baby's safety.
Prioritizing nutrition and hydration is crucial, as maintaining a balanced diet and staying well-hydrated can help prevent migraine and support both your health and your baby's growth.

One of the most effective ways to manage migraine while nursing is through safe lifestyle adjustments that promote natural relief.
Start by ensuring proper hydration, as breastfeeding can easily lead to dehydration, which might trigger migraine.
Keep a mineral water bottle handy and set reminders to drink regularly. Supplement with additional minerals, electrolytes and trace minerals were needed.
Proper nutrition is equally vital. Focus on a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients to support both your health and milk production. Again, add high quality nutrients and supplements, if it makes you feel even better.
Maintaining a headache diary can be important.
By tracking your migraine patterns, you'll identify triggers and understand what lifestyle changes work best for you.
Incorporating stress management techniques, like meditation or deep-breathing exercises, can help reduce migraine frequency and intensity, especially when your sleep is disrupted by the new baby
Stress is a well-known migraine trigger, and even a few minutes a day can make a difference.
Regular movement, such as walking or gentle stretching, can also play a crucial role in managing migraine.
It boosts endorphins and promotes better sleep, both of which can help reduce migraine occurrence.
Proven Non-Drug Therapies
Non-pharmacological approaches can effectively manage your symptoms, providing natural relief while keeping your baby safe.
As mentioned, lifestyle modifications like maintaining a regular sleep schedule and keeping mealtimes consistent to help stabilize your routine.
Proper hydration is crucial, as breastfeeding can deplete your fluid levels, potentially triggering migraine.
Biofeedback techniques can teach you to control physiological functions, potentially reducing migraine frequency and intensity.
These methods empower you to manage stress better, a common migraine trigger.
Also, consider incorporating hot or cold compresses to alleviate discomfort.
While exploring these options, remain cautious with certain treatments like aromatherapy, especially those involving essential oils, as they may not be suitable during breastfeeding.
Nutrition and Hydration Strategies
It's essential to focus on both nutrition and hydration to support your overall well-being.
We can not emphasize enough that hydration is vital. Drinking enough mineralized water is crucial because even mild dehydration can trigger headaches. Aim to drink fluids consistently throughout the day.
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients helps prevent energy and nutrient deficiencies. Incorporate enough protein, healthy fats, fruits, and colorful vegetables to support maternal nutrition, keeping both you and your baby healthy.
Animal sources of foods tend to have the most bioavailable forms of important nutrients, which can be important during breastfeeding.
MigraKet contains a lot of minerals, electrolytes and nutrients that are vital for breastmilk and development, in addition to ketone bodies, which are important for the development of a baby's brain.
It can help manage migraine as well as delivers many bioavailable nutrients that are important during this period and may be an additional tool in your toolbox as a breastfeeding migraine mother.
Consult with health care providers to tailor a nutrition plan that meets your unique needs. They can help identify any deficiencies and suggest dietary adjustments.
Medication Safety for Nursing Mothers
When managing migraine while breastfeeding, it's important to choose pain relievers that are safe for both you and your baby.
Breastfeeding-Compatible Pain Relievers
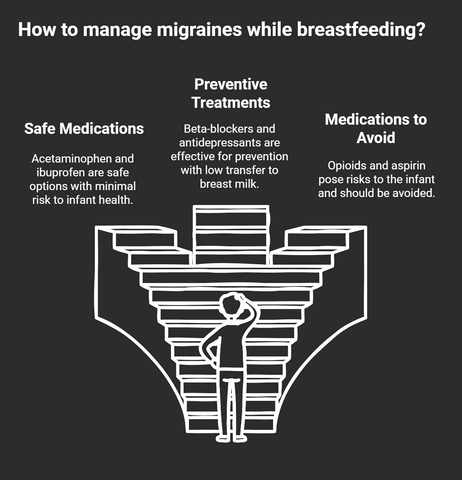
When considering acute treatments for migraine relief, acetaminophen often comes recommended as a primary option.
It's a safe medication choice with a proven track record of minimal risk to infant health outcomes.
You might also consider ibuprofen, another medication option that is considered safe, known for its low transfer rate into breast milk.
These medications offer an effective way to manage pain without necessarily compromising your baby's well-being.
It's always best to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any medication, especially during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
They can help ensure you're using treatments that align with your specific needs while keeping your baby safe.
Taking these steps helps maintain your health and your baby's safety.
By carefully selecting breastfeeding-compatible pain relievers, you can better manage migraine symptoms and focus on the joys of motherhood.
As you explore options for managing migraine while breastfeeding, you might find yourself considering not just immediate relief but also long-term prevention strategies.
It's a delicate balance to maintain your health while ensuring your baby's safety. Fortunately, several preventive treatments are deemed safe for breast-feeding women.
- Propranolol and Metoprolol: These beta-blockers are often prescribed for migraine prevention. They're well-tolerated and have minimal transfer into breast milk, making them a reliable option.
- Amitryptyline: This antidepressant isn't only effective for migraine prevention but also has a low transfer rate into breast milk. It can help manage migraine and improve mood, which can be beneficial in the postpartum period.
- Sertraline: Known for its safety profile, sertraline is another antidepressant that can aid in migraine prevention. It's particularly useful if you're dealing with postpartum depression alongside migraine.
While these medications are considered safe for the baby, they can certainly come with side effects. In any case, it's vital to consult your healthcare provider to tailor a plan that suits your needs.
Medications to Avoid While Nursing
Some migraine drugs can have adverse effects on infants, so knowing the safety considerations is key.
Opioids, for instance, should be avoided due to their potential for causing sedation and respiratory issues in your baby.
Similarly, aspirin poses risks, such as Reye's syndrome, making it a less-than-ideal choice during breastfeeding.
It's important to consult with your healthcare provider to identify which medications are safe and effective for you.
While some medications are necessary for managing migraine, their safety during breastfeeding must be carefully considered.
Always weigh the benefits against potential risks, and explore alternative treatments when possible.
Timing your medication intake right after nursing can also help minimize exposure for your baby.
This strategy, along with using drugs with shorter half-lives, could offer a safer approach.
Smart Migraine Management Strategies During Breastfeeding
When managing migraine during breastfeeding, it's crucial to time your medications around your feeding schedule to minimize any potential impact on your baby.
Timing Medications Around Feeding Schedule
Begin by coordinating your drug therapies around your baby's feeding schedule. This way, you can minimize the amount of medication that transfers into your breast milk.
Opt for acute medications with shorter half-lives and schedule them right after nursing; this reduces the concentration of medication present in the milk during the next feeding.
Here are some practical tips:
- Take medications immediately after breastfeeding: This approach allows the drug to metabolize and reduce concentration by the time your baby is ready to nurse again.
- Choose medications with shorter half-lives: They clear from your system more quickly, limiting your baby's exposure.
- Consider combining breastfeeding with bottle feeding: If a medication requires a longer clearance time, supplement with expressed breast milk or formula as needed.
Managing migraine medications while breastfeeding may seem daunting, but focusing on timing strategies and careful medication management can help.
Monitoring Baby's Well-being
You might feel overwhelmed, but with proper monitoring and care, you can achieve a balance between migraine management and infant safety.
Start by keeping track of your baby's growth and development to ensure they're thriving.
Pay attention to their feeding patterns and any changes that could signal a concern.
|
Monitoring |
Considerations |
Actions |
|
Baby's Well-being |
Weight gain, development |
Regular pediatric check-ups |
|
Breast Milk Production |
Hydration, nutrition |
Consume balanced diet |
|
Preventive Medications |
Safety, side effects |
Consult healthcare provider |
Breastfeeding demands a lot from your body, making proper nutrition and hydration essential for both breast milk production and your own health.
Ensure you consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support milk supply and help prevent migraine.
When using preventive medications, choose those with a good safety profile for nursing mothers.
Discuss options with your healthcare provider to minimize risks.
Remember, by closely monitoring your baby's well-being and taking care of yourself, you're setting the foundation for a healthy breastfeeding journey.
You're not alone in this—you've got the tools and support to make it work.
Building a Sustainable Care Plan
You might've experienced migraine relief during pregnancy due to high estrogen levels, but post-birth, things can change.
Non-pharmacological approaches are your first line of defense.
Keeping a headache diary helps identify triggers, while regular meals, sleep, and hydration and nutrition are essential. MigraKet can support with achieving nutrition and hydration goals.
Explore safe medication options if needed. Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are generally considered safe, and for more severe cases, sumatriptan is a reliable choice.
Always consult your healthcare provider to discuss treatment during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Monitoring and safety are key. Watch for any changes in your baby's behavior, like unusual lethargy or feeding difficulties.
Timing medication intake right after nursing can help minimize exposure.
Long-term management strategies will keep migraine at bay while ensuring your baby's safety.
Here are a few tips:
- Regular consultations: Stay in touch with healthcare providers to adjust your care plan as needed.
- Trigger avoidance: Identify and steer clear of known migraine triggers.
- Stress management: Develop relaxation techniques to maintain mental well-being.
Together, these strategies help create a sustainable care plan, ensuring both you and your baby thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
After exploring the information above, you may still have some questions about managing migraine while breastfeeding.
We’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions to address some of the most common concerns related to this topic.
How do migraine patterns typically change from pregnancy to breastfeeding?
While many women experience relief from migraine during pregnancy due to stable estrogen levels, the transition to breastfeeding can bring new challenges.
The shift from pregnancy hormones to postpartum hormone levels, combined with lack of sleep and the physical demands of nursing, can trigger new migraine patterns.
However, breastfeeding itself may help stabilize hormones and reduce migraine frequency compared to the immediate postpartum period.
How do Antiepileptic drugs affect human milk production and the breast-fed infant?
Antiepileptic drugs used for migraine prevention can transfer into human breast milk at varying levels.
The impact on breast-fed infants depends on factors like the specific medication, dosage, and timing of doses.
Some newer antiepileptic medications have lower excretion into breast milk and are considered safer for nursing mothers, but all should be carefully evaluated by a healthcare provider, especially for premature infants who may be more sensitive to medication exposure.
How does the menstrual cycle affect migraine while breastfeeding?
When menstruation returns during breastfeeding, some women experience changes in their migraine patterns due to hormonal fluctuations.
The return of the menstrual cycle can trigger severe attacks in some cases. However, continued breastfeeding may help moderate these hormonal shifts and potentially reduce migraine frequency compared to non-breastfeeding mothers.
What's the relationship between tension headaches and migraine in nursing mothers?
Nursing mothers often experience both tension headaches and migraine headaches, which can sometimes be difficult to distinguish.
Tension headaches may be triggered by physical stress from nursing positions and lack of sleep, while migraine typically have additional symptoms.
Understanding the difference is crucial for proper treatment, as management strategies may differ for each type.
How do doctors evaluate the transfer of drugs through Mother's Milk when prescribing migraine treatments?
Healthcare providers assess several factors when prescribing migraine medications to breastfeeding mothers, including:
- The medication's molecular size and ability to pass into breast milk
- The drug's half-life and peak levels in breast milk
- The infant's age and ability to metabolize medications
- The timing of doses relative to feeding schedules
- The mother's severity of migraine and need for treatment
How does previous migraine therapy during pregnancy affect treatment choices while breastfeeding?
Treatment history during pregnancy often influences medication choices during breastfeeding.
Medications that proved safe and effective during pregnancy are often considered first, provided they're also safe for breast-fed infants.
Healthcare providers will evaluate the outcome in women who used specific medications during pregnancy to help inform treatment decisions during lactation.
Conclusion
Managing migraine while breastfeeding is challenging but achievable with the right approach.
Through a combination of lifestyle adjustments, proper nutrition, safe medications, and careful monitoring, you can effectively handle migraine while maintaining your nursing journey.
Remember that taking care of yourself is essential for your baby's well-being too.
Work closely with your healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that balances migraine management with breastfeeding safety.
With proper support and the strategies discussed in this article, you can hopefully navigate this phase of motherhood successfully while keeping both you and your baby healthy.





